BacktotheBasic - 스택(stack)_1-Array를 이용한 스택 구현
March 02, 2018
스택 (stack)
스택은 큐와 함께 소프트웨어 분s야에서 엄청나게 중요한 역할을 한다.
자동 메모리가 스택을 기반으로 동작하고, 대부분의 네트워크 프로토콜도 스택을 기반으로 구성되어있다고 한다.
가장 흔하게 접할 수 있는 예가 javascript 콜스택이 아닐까 싶다.
스택은 첨에 들어간 것이 가장 나중에 나오도록 되어 있다.(FILO : Firts In Last Out or LIFO: Last In First Out)
즉 삽입과 삭제가 한쪽 끝에서만 이루어 지는것이다.
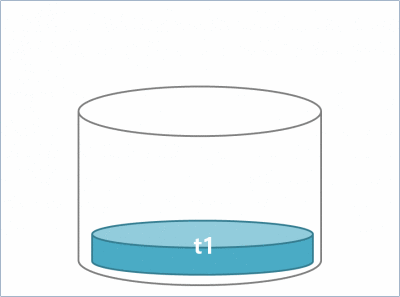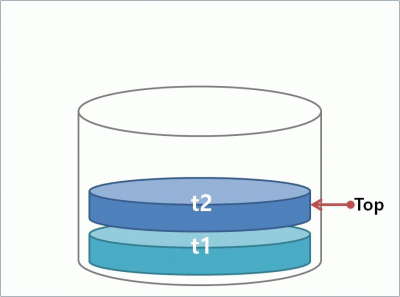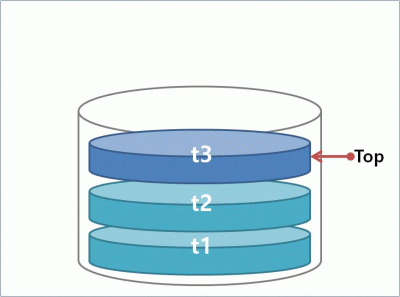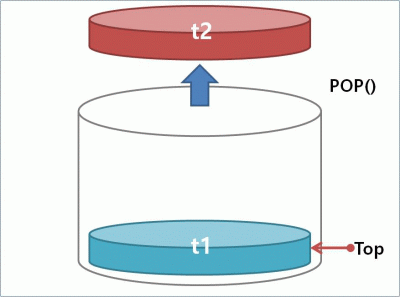
stack을 배열과 링크드로 구현해 보겠다.
우선 인터페이스를 만들어 준다 java.util.Stack을 보니
stack에 있는 E 를 꺼내는 pop()
요소를 넣는 push()
top요소를 가져오는 peek() (E를 가져오기만 하고 빼내진 않는다.)
빈스택인지 확인하는 empty()
해당 E가 몇번째에 위치하고 있는지 확인하는 search()
메소드를 가지고 있어서 인터페이스에 Stack은 위의 메소드를 가지는 것으로 정의해 주었다.
codebox
Stack.java
package task.structure;
public interface Stack {
public void pop();
public void push();
public Object peek();
public boolean empty();
public int search();
}
생성자
public ArrayStack(int max) {
this.top = -1;
this.arrStack = new Object[max];
}
push() 구현
@Override
public void push(Object input) {
this.arrStack[this.top+1] = input;
this.top++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayStack mystack = new ArrayStack(4);
mystack.push("1");
System.out.println(mystack.toString()); //[1, null, null, null]
mystack.push("2");
mystack.push("3");
mystack.push("4");
System.out.println(mystack.toString()); //[1, 2, 3, 4]
mystack.push("5"); //error!!!!!!
}배열로 구현한 stack은 처음 설정해준 사이즈 이상으로 요소를 넣게 되면 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 이라는 Exception이 나타난다.
empty와 search 구현
@Override
public boolean empty() {
if(top < 0 ){ // 0 일때
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public int search(Object input) {
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("비어있는 stack입니다.");
}
int i = this.top;
while(i > -1 ){
if(input.equals(this.arrStack[i])){
break;
}
i--;
}
return i;
}
empty() 메소드는 스택이 빈 스택인지를 확인하고 빈스택이면 true,
스택에 무언가 들어가 있으면 false를 반환.
search는 빈스택이 아니면
위에서 부터 stack안에 있는 데이터를 비교해서 동일하면 index를 반환.
pop과 peek
@Override
public Object pop() {
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("비어있는 stack입니다." );
}
this.arrStack[top] = null;
return this.arrStack[top--];
}
@Override
public Object peek() {
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("비어있는 stack입니다." );
}
return this.arrStack[top];
}
pop과 peek 메소드는 두개다 stack의 top(최근에 넣은 index)에 해당하는 데이터를 return한다.
두 메소드의 다른 점은 pop은 아예 빼내는 거고 (후치연산자로 top– 를 해줌)
peek는 위에있는것을 그냥 확인하는 것이다(top값의 변화가 없음.).
ArrayStack.java
package task.structure;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class ArrayStack implements Stack{
private int top;
private Object[] arrStack;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayStack mystack = new ArrayStack(4);
mystack.push("1");
try{
System.out.println(mystack.toString()); //[1, null, null, null]
mystack.push("2");
mystack.push("3");
mystack.push("4");
System.out.println(mystack.toString()); //[1, null, null, null]
mystack.push("5"); //your stack is already full.
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println("your stack is already full.");
}
try{
System.out.println( "search 3 : " + mystack.search("3") ); //search 3 : 1
mystack.pop();
mystack.pop();
mystack.pop();
System.out.println(mystack.toString());//[1]
System.out.println(mystack.peek().toString()); //1
System.out.println(mystack.toString());//[1]
mystack.pop();
System.out.println(mystack.toString());//[]
mystack.pop(); // This stack is Empty Now!
}catch (EmptyStackException ex) {
System.out.println("This stack is Empty Now!");
}
}
public ArrayStack(int max) {
this.top = -1;
this.arrStack = new Object[max];
}
@Override
public Object pop() {
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("비어있는 stack입니다." );
}
this.arrStack[top] = null;
return this.arrStack[top--];
}
@Override
public void push(Object input) {
try{
this.arrStack[this.top+1] = input;
this.top++;
}catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
throw e;
}
}
@Override
public Object peek() {
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("비어있는 stack입니다." );
}
return this.arrStack[top];
}
@Override
public boolean empty() {
if(top < 0 ){ // 0 일때
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public int search(Object input) {
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("비어있는 stack입니다.");
}
int i = this.top;
while(i > -1 ){
if(input.equals(this.arrStack[i])){
break;
}
i--;
}
return i;
}
public String toString(){
if(empty()){
return "[]";
}
String str= "[";
int i = 0;
while(i < this.top){
str += this.arrStack[i].toString() + ",";
i++;
}
str += this.arrStack[i];
return str+="]";
}
}
class EmptyStackException extends RuntimeException{
public EmptyStackException() {
super();
}
EmptyStackException(String message){
super(message);
}
}